Cannabis Components: Cannabinoids + Terpenes

The cannabis plant isn’t a new trend. It’s been grown and used across the world for thousands of years, and it holds a unique chemistry that makes cannabis so different from other plants. Its cannabinoids give it unique psychoactive properties and additional benefits, while its terpene profiles give it the distinct aromas we’ve all come to know (and love).
Cannabinoids
Cannabis’ chemistry makes the plant unique through its cannabinoids, the most well-known of 100+ cannabinoids being THC and CBD.
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) is responsible for delivering the psychoactive high obtained when using cannabis, bringing along changes in mood, perception, and often euphoria. THC also contains many of the beneficial components that come with consuming cannabis.
- CBD (Cannabidiol) on the other hand does not contain the psychoactive high that THC does, but does accompany THC in added benefits and may provide noticeable relaxation without mind altering effects.
- Minor Cannabinoids are growing in popularity as more research unfolds. Like CBD, CBG does not deliver psychoactive effects, but is currently being researched to better understand its potential medical benefits. Other minor cannabinoids like CBN, which is undergoing research on its sleep aid benefits, and THCV are also being researched in order to find out what they can offer to consumers. There are hundreds of cannabinoids that harbor so much potential, it’s just up to time and research to uncover what they can do.
- The entourage effect happens when cannabis compounds interact synergistically with each other to magnify their benefits. This means that while the CBD cannabinoid contains properties on its own, it is heightened when paired with THC and vice versa. Additional compounds called terpenes, found in cannabis and throughout nature, also enhance the cannabis experience. See cannabinoid profiles listed in relevant product pages.


Terpenes
Terpenes are compounds that are found in plants and animals, producing unique aromas and flavors. For instance, pinene is the dominant terpene in pine needles, giving it that distinct and recognizable smell. Different cannabis strains contain various levels of terpenes, giving them each their unique taste and smell, allowing enthusiasts to dial in on what they prefer. You might have heard of some popular terpenes found in cannabis like limonene, which gives off a bright citrus aroma, or myrcene which typically gives off that earthy dank scent. Caryophyllene, linalool, pinene, terpinolene, and ocimene are also common terpenes found in our cannabis. There have been recent studies that show certain terpenes in cannabis can actually enhance the effects of the cannabinoids they are paired with, sometimes even heightening the experience. For example, limonene is believed to be a great pairing for sativa strains due to its uplifting effects. See terpene profiles listed in relevant product pages.


The Endocannabinoid System
Our endocannabinoid system (ECS) controls many of our most important body functions, including memory, sleep, inflammation, emotional processing, temperature control, eating, and immune response. ECS is a network of chemical signals and receptors throughout our body that are triggered by the production of endocannabinoids, which our bodies naturally produce for the function needed. These endocannabinoids have a similar cellular structure to cannabinoid molecules in the cannabis plant. THC and other cannabinoids are able to take effect by attaching to these receptors in our bodies much like our naturally occurring endocannabinoids do.
Cannabis Botany
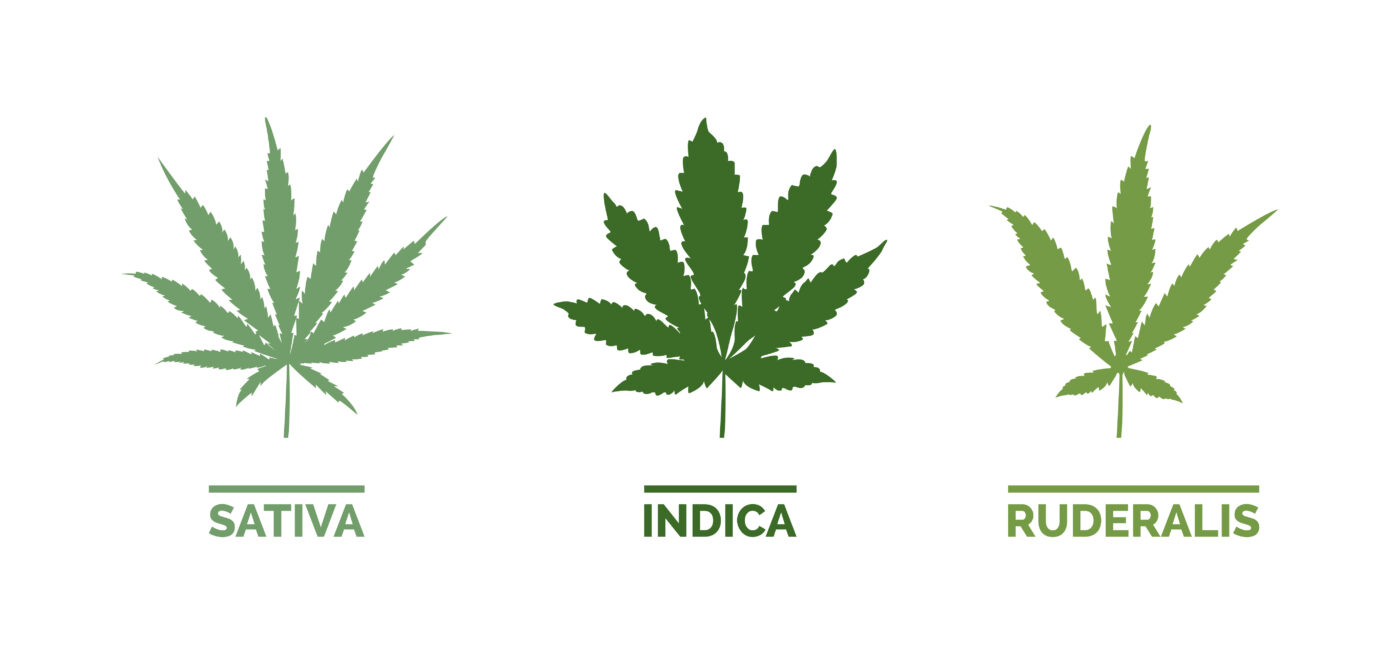
Cannabis is generally considered a dioecious plant, meaning some plants have staminate “male” flowers and some have pistillate “female” flowers. Sometimes you find cannabis plants that are monoecious, where there are both male and female components within the same plant. Also noteworthy is that cannabis has small hairs called trichomes which, on female plants, produce and harbor the majority of the plant’s cannabinoid and terpene compounds. While there is some disagreement among the scientific community, cannabis is typically classified in three different species: cannabis sativa, cannabis indica, and cannabis ruderalis – all of which can be interbred with each other to create hybridization. Sativa and indica are the two species commonly used in the cannabis industry, sativa growing as a skinny, thin-leafed plant, and indica growing as a shorter, broad-leafed plant. Ruderalis is a typically lower-THC form of cannabis that isn’t light dependent in the same way the other two species are. Learn about our cultivation.